Zeitgeist Real Estate
Smart Building Management for the Real Estate Industry

Real Estate actors can evaluate material suitability and rapidly see the influence of their design decisions on associated carbon emissions.
The biggest opportunity for technology to manage our carbon footprint is by having tools like Forma, that will allow us to analyze our projects in real time, as we’re designing them.
Being able to have that information, that feedback, as we’re doing the design work is really what’s going to enable us to achieve the goals that we need to reduce the carbon impact of the built environment.

***Learning Outcomes***
1.Understanding AI's Role in Urban Planning and Real Estate Development: Students gain firsthand experience in how AI can optimize complex urban development challenges.
By witnessing the algorithm at work, they see how AI processes constraints and opportunities in ways that are often different from human intuition.
2. Human vs. Machine Thinking: The workshop provides a fascinating contrast between human creativity and machine logic: Students observe the strengths and limitations of both approaches: where human designers bring creativity and empathy to urban planning, the AI focuses on efficiency, rule compliance, and optimization.
3. Legal and Architectural Awareness: Students deepen their understanding of the critical constraints in urban development, such as zoning laws, building codes, environmental considerations, and infrastructure planning. They must apply these in their city designs, just as the AI does.
4. Problem-Solving and Innovation: The course encourages students to think creatively about real-world urban problems. The head-to-head comparison with the AI forces students to consider new approaches, question traditional methods, and innovate in ways that machines cannot.
5. Collaborative and Competitive Learning
The "vs." framework sparks both collaboration and competition. Students learn from each other and from the AI-generated results, fostering an environment of constant iteration, improvement, and learning from mistakes.
6. Future-Proof Skills
Students leave the course equipped with future-proof skills at the intersection of urban planning, architecture, and AI. They understand not only how to design cities, but also how to collaborate with and leverage AI tools in their future careers.
***Key Insights from the Workshop***
At the end of the course, a comparative analysis reveals fascinating insights:
a) Efficiency vs. Creativity: The AI often produces more efficient layouts, optimizing land use and infrastructure. However, human designs tend to reflect more nuanced social and cultural considerations.
b)Legal and Practical Constraints: The AI never overlooks legal constraints, whereas students sometimes need reminders. This demonstrates the importance of integrating AI as a compliance tool in real-world projects.
c)Hybrid Solutions: The most exciting outcome is the realization that the best urban plans emerge from a collaborative human-AI process—leveraging the strengths of both to create sustainable, livable cities.
In essence, this class prepares future architects, urban planners, and Real Estate developers to navigate the rapidly evolving world of real estate and city building, where human expertise and AI tools must work hand-in-hand to shape the cities of tomorrow.

Per 1. September 2025 tritt Dr. Andrea González die Leitung der neu geschaffene Kompetenzgruppe Smart Building Management (SBM) am Institut für Facility Management an. Diese Gruppe beschäftigt sich mit der intelligenten, nachhaltigen und nutzerzentrierten Entwicklung, Nutzung und Bewirtschaftung von Gebäuden und Arealen. Im Fokus stehen digitale Technologien, datenbasierte Services und integrale Strategien entlang des gesamten Immobilienlebenszyklus.
Expertin mit langjähriger Erfahrung weltweit
Andrea González verfügt über mehr als 15 Jahre internationale Erfahrung in den Bereichen Städtebau, Immobilienentwicklung, Architektur, Nachhaltigkeit und Digitalisierung. Dabei hat sie auch komplexe Immobilienprojekte in Europa und Asien umgesetzt. Ihr fundiertes Wissen erstreckt sich über alle Phasen des Immobilienlebenszyklus. Dazu gehören Standortanalyse, Akquisition, Konzeptentwicklung, Planung, Bau, Betrieb und Sanierung sowie die strategische Umnutzung und Verwertung. Besonderen Fokus legt sie auf innovative Smart-Building-Strategien. Ihre Führungserfahrung reicht von der Projektleitung in Immobilienentwicklungsunternehmen bis zur Gesamtverantwortung als Head of Real Estate und Architektur bei der Firma Uster AG.
Brückenbauerin zwischen Praxis und Forschung
Parallel zu ihrer praktischen Tätigkeit engagiert sie sich seit vielen Jahren in Forschung und Lehre. Ihre interdisziplinäre Kompetenz, internationale Erfahrung und strategische Denkweise machen sie zu einer Brückenbauerin zwischen Praxis und Forschung in den Bereichen Architektur, Smart Buildings, Smart Cities, Digitalisierung und Nachhaltigkeit.

Implementation of BIM and AI
In this project, Building Information Modeling (BIM) was used to optimize the design and construction processes. BIM allowed for precise modeling of the steep terrain, enabling efficient planning and visualization of the modular structures and their integration into the challenging site conditions. The technology also facilitated seamless coordination among various teams, ensuring sustainability goals were met while maintaining design integrity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) was employed to analyze the environmental impact of materials and construction methods. AI algorithms were used to simulate energy efficiency, assess structural performance, and optimize material usage. This ensured that the project adhered to sustainable practices while achieving a harmonious balance with the natural forested environment. AI also supported decision-making during the design phase, predicting how the prefabricated components would interact and perform in the final assembly, reducing waste and enhancing overall project efficiency.

In our session at CUREM - Center for Urban & Real Estate Management, University of Zurich, we explored strategies for real estate development, particularly from the perspective of investors. The focus was on how digital tools are revolutionizing planning, analysis, and decision-making in the real estate sector.
Key Points from Today’s Discussion:
🔹 Data-Driven Analyses: Tools for market and site analysis (e.g., GIS systems) help investors make informed decisions about locations and target markets.
🔹 Financial Modeling: Tools like Excel with macros or Python scripts enable precise profitability calculations, sensitivity analyses, and scenario simulations.
🔹 Project Visualization: Software like BIM and AI (Building Information Modeling + Artificial Intelligence) enhances project visualization, making it easier for stakeholders to understand and engage.
🔹 Risk Management: Digital tools aid in identifying risks during the early planning stages, leveraging simulations and monitoring market trends.
A key takeaway from the session was that successful real estate investment relies not only on numbers but also on the ability to integrate innovative approaches, anticipate risks, and leverage technological advancements.
Whether analyzing market opportunities, optimizing development processes, or securing financing, digital tools are essential for giving investors a competitive edge.

Digital terrain modelling is transforming the way architects, planners, and engineers interact with the natural world. 🌿 From visualizing complex topographies to simulating realistic landscapes, advanced tools make it easier than ever to shape ideas into reality.
✨ Why Terrain Modelling Matters:
Precision in planning 🌟
Seamless integration with GIS data 📊
Efficient environmental analysis 🌲
Stunning visualizations for impactful presentations 🎥
🎯 Popular Tools to Explore:
AutoCAD Civil 3D: For infrastructure design and drafting.
SketchUp + Plugins: Quick 3D terrain creation.
Rhino + Grasshopper: Precision + automation for custom forms.
ArcGIS: Ideal for GIS-based topographical insights.
💡 Whether you're designing for architecture, urban planning, or ecological restoration, mastering digital terrain modelling opens up a world of possibilities.
Show us your terrain-inspired projects! Drop your designs or tag a fellow creator who’d love this. 📷👇
#DigitalDesign #TerrainModelling #CAD #GIS #Architecture #3DModelling #SustainableDesign

🔹 AI in Design & Planning
Artificial Intelligence played a central role, from generating design concepts to optimizing layouts and material usage. Tools like AI-enhanced visualization software allowed us to experiment with ideas quickly and efficiently, ensuring the final design was both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
🔹 Digital Fabrication & Craftsmanship
Even the physical wooden model—an essential part of architectural competitions—was crafted using digital fabrication techniques, informed by AI-based simulations. This seamless integration of traditional craftsmanship with cutting-edge technologies like 3D printing and precision CNC machining highlights the future of architectural practice.

🔹 Data-Driven Planning for People-Centered Design
The project began with a comprehensive statistical demographic study, analyzing population shifts, age distribution, and economic patterns in the affected areas. These insights informed every decision, ensuring that the reconstructed spaces cater to the actual needs of the community—from housing to public spaces, and even economic infrastructure.
🔹 Handcrafted with Purpose
While data shaped the framework, the project was brought to life through handcrafted techniques that reflect the rich cultural heritage of Onagawa. Local materials and traditional construction methods were used alongside modern technologies, creating structures that honor the past while looking toward the future.
🔹 Rebuilding Lives, Not Just Cities
The project emphasizes community empowerment, involving residents in the reconstruction process. This hands-on approach fosters a sense of ownership and belonging, ensuring that the spaces are more than buildings—they are homes, hubs of connection, and symbols of resilience.
🔹 A Model for Post-Disaster Recovery
The Onagawa Project stands as a beacon of how thoughtful design, powered by statistical rigor and human craftsmanship, can drive meaningful recovery. It demonstrates that rebuilding after a catastrophe is not just about physical infrastructure but also about nurturing the social and cultural fabric of a community.
By blending data-driven insights with the art of human touch, the Onagawa Project showcases the potential to transform tragedy into an opportunity for rebirth, creating spaces that inspire and endure.
#OnagawaProject #PostDisasterRecovery #SustainableReconstruction #FukushimaRecovery #CommunityDrivenDesign #HandcraftedArchitecture #ResilienceThroughDesign

In this groundbreaking project, AI and BIM come together to streamline processes, optimize designs, and ensure seamless collaboration among architects, engineers, and developers. AI’s ability to process vast datasets enables predictive analysis and informed decision-making, from site selection to energy-efficient building designs. Meanwhile, BIM offers an integrated approach to project management, providing a shared platform that fosters real-time coordination and minimizes errors throughout the lifecycle of the development.
Autodesk Forma’s sophisticated tools enhance every phase of the project, from conceptualization to execution, emphasizing sustainability and innovation. By leveraging Archicad’s dynamic design capabilities, the project achieves a balance between aesthetic excellence and functional efficiency, creating spaces that are not just visually appealing but also environmentally responsible.
This Zurich Lake development is more than a construction project—it’s a vision of what’s possible when technology meets creativity, pushing the boundaries of urban planning and sustainable living. Watch the video to explore how AI and BIM are not just supporting construction but fundamentally transforming it, paving the way for smarter, greener, and more integrated communities.
#RealEstateInnovation #AIinConstruction #BIM #ZurichLakeDevelopment #SustainableArchitecture #FutureOfConstruction

Real Estate actors can evaluate material suitability and rapidly see the influence of their design decisions on associated carbon emissions.
The biggest opportunity for technology to manage our carbon footprint is by having tools like Forma, that will allow us to analyze our projects in real time, as we’re designing them.
Being able to have that information, that feedback, as we’re doing the design work is really what’s going to enable us to achieve the goals that we need to reduce the carbon impact of the built environment.

***Learning Outcomes***
1.Understanding AI's Role in Urban Planning and Real Estate Development: Students gain firsthand experience in how AI can optimize complex urban development challenges.
By witnessing the algorithm at work, they see how AI processes constraints and opportunities in ways that are often different from human intuition.
2. Human vs. Machine Thinking: The workshop provides a fascinating contrast between human creativity and machine logic: Students observe the strengths and limitations of both approaches: where human designers bring creativity and empathy to urban planning, the AI focuses on efficiency, rule compliance, and optimization.
3. Legal and Architectural Awareness: Students deepen their understanding of the critical constraints in urban development, such as zoning laws, building codes, environmental considerations, and infrastructure planning. They must apply these in their city designs, just as the AI does.
4. Problem-Solving and Innovation: The course encourages students to think creatively about real-world urban problems. The head-to-head comparison with the AI forces students to consider new approaches, question traditional methods, and innovate in ways that machines cannot.
5. Collaborative and Competitive Learning
The "vs." framework sparks both collaboration and competition. Students learn from each other and from the AI-generated results, fostering an environment of constant iteration, improvement, and learning from mistakes.
6. Future-Proof Skills
Students leave the course equipped with future-proof skills at the intersection of urban planning, architecture, and AI. They understand not only how to design cities, but also how to collaborate with and leverage AI tools in their future careers.
***Key Insights from the Workshop***
At the end of the course, a comparative analysis reveals fascinating insights:
a) Efficiency vs. Creativity: The AI often produces more efficient layouts, optimizing land use and infrastructure. However, human designs tend to reflect more nuanced social and cultural considerations.
b)Legal and Practical Constraints: The AI never overlooks legal constraints, whereas students sometimes need reminders. This demonstrates the importance of integrating AI as a compliance tool in real-world projects.
c)Hybrid Solutions: The most exciting outcome is the realization that the best urban plans emerge from a collaborative human-AI process—leveraging the strengths of both to create sustainable, livable cities.
In essence, this class prepares future architects, urban planners, and Real Estate developers to navigate the rapidly evolving world of real estate and city building, where human expertise and AI tools must work hand-in-hand to shape the cities of tomorrow.

Per 1. September 2025 tritt Dr. Andrea González die Leitung der neu geschaffene Kompetenzgruppe Smart Building Management (SBM) am Institut für Facility Management an. Diese Gruppe beschäftigt sich mit der intelligenten, nachhaltigen und nutzerzentrierten Entwicklung, Nutzung und Bewirtschaftung von Gebäuden und Arealen. Im Fokus stehen digitale Technologien, datenbasierte Services und integrale Strategien entlang des gesamten Immobilienlebenszyklus.
Expertin mit langjähriger Erfahrung weltweit
Andrea González verfügt über mehr als 15 Jahre internationale Erfahrung in den Bereichen Städtebau, Immobilienentwicklung, Architektur, Nachhaltigkeit und Digitalisierung. Dabei hat sie auch komplexe Immobilienprojekte in Europa und Asien umgesetzt. Ihr fundiertes Wissen erstreckt sich über alle Phasen des Immobilienlebenszyklus. Dazu gehören Standortanalyse, Akquisition, Konzeptentwicklung, Planung, Bau, Betrieb und Sanierung sowie die strategische Umnutzung und Verwertung. Besonderen Fokus legt sie auf innovative Smart-Building-Strategien. Ihre Führungserfahrung reicht von der Projektleitung in Immobilienentwicklungsunternehmen bis zur Gesamtverantwortung als Head of Real Estate und Architektur bei der Firma Uster AG.
Brückenbauerin zwischen Praxis und Forschung
Parallel zu ihrer praktischen Tätigkeit engagiert sie sich seit vielen Jahren in Forschung und Lehre. Ihre interdisziplinäre Kompetenz, internationale Erfahrung und strategische Denkweise machen sie zu einer Brückenbauerin zwischen Praxis und Forschung in den Bereichen Architektur, Smart Buildings, Smart Cities, Digitalisierung und Nachhaltigkeit.

Implementation of BIM and AI
In this project, Building Information Modeling (BIM) was used to optimize the design and construction processes. BIM allowed for precise modeling of the steep terrain, enabling efficient planning and visualization of the modular structures and their integration into the challenging site conditions. The technology also facilitated seamless coordination among various teams, ensuring sustainability goals were met while maintaining design integrity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) was employed to analyze the environmental impact of materials and construction methods. AI algorithms were used to simulate energy efficiency, assess structural performance, and optimize material usage. This ensured that the project adhered to sustainable practices while achieving a harmonious balance with the natural forested environment. AI also supported decision-making during the design phase, predicting how the prefabricated components would interact and perform in the final assembly, reducing waste and enhancing overall project efficiency.

In our session at CUREM - Center for Urban & Real Estate Management, University of Zurich, we explored strategies for real estate development, particularly from the perspective of investors. The focus was on how digital tools are revolutionizing planning, analysis, and decision-making in the real estate sector.
Key Points from Today’s Discussion:
🔹 Data-Driven Analyses: Tools for market and site analysis (e.g., GIS systems) help investors make informed decisions about locations and target markets.
🔹 Financial Modeling: Tools like Excel with macros or Python scripts enable precise profitability calculations, sensitivity analyses, and scenario simulations.
🔹 Project Visualization: Software like BIM and AI (Building Information Modeling + Artificial Intelligence) enhances project visualization, making it easier for stakeholders to understand and engage.
🔹 Risk Management: Digital tools aid in identifying risks during the early planning stages, leveraging simulations and monitoring market trends.
A key takeaway from the session was that successful real estate investment relies not only on numbers but also on the ability to integrate innovative approaches, anticipate risks, and leverage technological advancements.
Whether analyzing market opportunities, optimizing development processes, or securing financing, digital tools are essential for giving investors a competitive edge.

Digital terrain modelling is transforming the way architects, planners, and engineers interact with the natural world. 🌿 From visualizing complex topographies to simulating realistic landscapes, advanced tools make it easier than ever to shape ideas into reality.
✨ Why Terrain Modelling Matters:
Precision in planning 🌟
Seamless integration with GIS data 📊
Efficient environmental analysis 🌲
Stunning visualizations for impactful presentations 🎥
🎯 Popular Tools to Explore:
AutoCAD Civil 3D: For infrastructure design and drafting.
SketchUp + Plugins: Quick 3D terrain creation.
Rhino + Grasshopper: Precision + automation for custom forms.
ArcGIS: Ideal for GIS-based topographical insights.
💡 Whether you're designing for architecture, urban planning, or ecological restoration, mastering digital terrain modelling opens up a world of possibilities.
Show us your terrain-inspired projects! Drop your designs or tag a fellow creator who’d love this. 📷👇
#DigitalDesign #TerrainModelling #CAD #GIS #Architecture #3DModelling #SustainableDesign

🔹 AI in Design & Planning
Artificial Intelligence played a central role, from generating design concepts to optimizing layouts and material usage. Tools like AI-enhanced visualization software allowed us to experiment with ideas quickly and efficiently, ensuring the final design was both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
🔹 Digital Fabrication & Craftsmanship
Even the physical wooden model—an essential part of architectural competitions—was crafted using digital fabrication techniques, informed by AI-based simulations. This seamless integration of traditional craftsmanship with cutting-edge technologies like 3D printing and precision CNC machining highlights the future of architectural practice.

🔹 Data-Driven Planning for People-Centered Design
The project began with a comprehensive statistical demographic study, analyzing population shifts, age distribution, and economic patterns in the affected areas. These insights informed every decision, ensuring that the reconstructed spaces cater to the actual needs of the community—from housing to public spaces, and even economic infrastructure.
🔹 Handcrafted with Purpose
While data shaped the framework, the project was brought to life through handcrafted techniques that reflect the rich cultural heritage of Onagawa. Local materials and traditional construction methods were used alongside modern technologies, creating structures that honor the past while looking toward the future.
🔹 Rebuilding Lives, Not Just Cities
The project emphasizes community empowerment, involving residents in the reconstruction process. This hands-on approach fosters a sense of ownership and belonging, ensuring that the spaces are more than buildings—they are homes, hubs of connection, and symbols of resilience.
🔹 A Model for Post-Disaster Recovery
The Onagawa Project stands as a beacon of how thoughtful design, powered by statistical rigor and human craftsmanship, can drive meaningful recovery. It demonstrates that rebuilding after a catastrophe is not just about physical infrastructure but also about nurturing the social and cultural fabric of a community.
By blending data-driven insights with the art of human touch, the Onagawa Project showcases the potential to transform tragedy into an opportunity for rebirth, creating spaces that inspire and endure.
#OnagawaProject #PostDisasterRecovery #SustainableReconstruction #FukushimaRecovery #CommunityDrivenDesign #HandcraftedArchitecture #ResilienceThroughDesign

In this groundbreaking project, AI and BIM come together to streamline processes, optimize designs, and ensure seamless collaboration among architects, engineers, and developers. AI’s ability to process vast datasets enables predictive analysis and informed decision-making, from site selection to energy-efficient building designs. Meanwhile, BIM offers an integrated approach to project management, providing a shared platform that fosters real-time coordination and minimizes errors throughout the lifecycle of the development.
Autodesk Forma’s sophisticated tools enhance every phase of the project, from conceptualization to execution, emphasizing sustainability and innovation. By leveraging Archicad’s dynamic design capabilities, the project achieves a balance between aesthetic excellence and functional efficiency, creating spaces that are not just visually appealing but also environmentally responsible.
This Zurich Lake development is more than a construction project—it’s a vision of what’s possible when technology meets creativity, pushing the boundaries of urban planning and sustainable living. Watch the video to explore how AI and BIM are not just supporting construction but fundamentally transforming it, paving the way for smarter, greener, and more integrated communities.
#RealEstateInnovation #AIinConstruction #BIM #ZurichLakeDevelopment #SustainableArchitecture #FutureOfConstruction

Real Estate actors can evaluate material suitability and rapidly see the influence of their design decisions on associated carbon emissions.
The biggest opportunity for technology to manage our carbon footprint is by having tools like Forma, that will allow us to analyze our projects in real time, as we’re designing them.
Being able to have that information, that feedback, as we’re doing the design work is really what’s going to enable us to achieve the goals that we need to reduce the carbon impact of the built environment.

***Learning Outcomes***
1.Understanding AI's Role in Urban Planning and Real Estate Development: Students gain firsthand experience in how AI can optimize complex urban development challenges.
By witnessing the algorithm at work, they see how AI processes constraints and opportunities in ways that are often different from human intuition.
2. Human vs. Machine Thinking: The workshop provides a fascinating contrast between human creativity and machine logic: Students observe the strengths and limitations of both approaches: where human designers bring creativity and empathy to urban planning, the AI focuses on efficiency, rule compliance, and optimization.
3. Legal and Architectural Awareness: Students deepen their understanding of the critical constraints in urban development, such as zoning laws, building codes, environmental considerations, and infrastructure planning. They must apply these in their city designs, just as the AI does.
4. Problem-Solving and Innovation: The course encourages students to think creatively about real-world urban problems. The head-to-head comparison with the AI forces students to consider new approaches, question traditional methods, and innovate in ways that machines cannot.
5. Collaborative and Competitive Learning
The "vs." framework sparks both collaboration and competition. Students learn from each other and from the AI-generated results, fostering an environment of constant iteration, improvement, and learning from mistakes.
6. Future-Proof Skills
Students leave the course equipped with future-proof skills at the intersection of urban planning, architecture, and AI. They understand not only how to design cities, but also how to collaborate with and leverage AI tools in their future careers.
***Key Insights from the Workshop***
At the end of the course, a comparative analysis reveals fascinating insights:
a) Efficiency vs. Creativity: The AI often produces more efficient layouts, optimizing land use and infrastructure. However, human designs tend to reflect more nuanced social and cultural considerations.
b)Legal and Practical Constraints: The AI never overlooks legal constraints, whereas students sometimes need reminders. This demonstrates the importance of integrating AI as a compliance tool in real-world projects.
c)Hybrid Solutions: The most exciting outcome is the realization that the best urban plans emerge from a collaborative human-AI process—leveraging the strengths of both to create sustainable, livable cities.
In essence, this class prepares future architects, urban planners, and Real Estate developers to navigate the rapidly evolving world of real estate and city building, where human expertise and AI tools must work hand-in-hand to shape the cities of tomorrow.

Per 1. September 2025 tritt Dr. Andrea González die Leitung der neu geschaffene Kompetenzgruppe Smart Building Management (SBM) am Institut für Facility Management an. Diese Gruppe beschäftigt sich mit der intelligenten, nachhaltigen und nutzerzentrierten Entwicklung, Nutzung und Bewirtschaftung von Gebäuden und Arealen. Im Fokus stehen digitale Technologien, datenbasierte Services und integrale Strategien entlang des gesamten Immobilienlebenszyklus.
Expertin mit langjähriger Erfahrung weltweit
Andrea González verfügt über mehr als 15 Jahre internationale Erfahrung in den Bereichen Städtebau, Immobilienentwicklung, Architektur, Nachhaltigkeit und Digitalisierung. Dabei hat sie auch komplexe Immobilienprojekte in Europa und Asien umgesetzt. Ihr fundiertes Wissen erstreckt sich über alle Phasen des Immobilienlebenszyklus. Dazu gehören Standortanalyse, Akquisition, Konzeptentwicklung, Planung, Bau, Betrieb und Sanierung sowie die strategische Umnutzung und Verwertung. Besonderen Fokus legt sie auf innovative Smart-Building-Strategien. Ihre Führungserfahrung reicht von der Projektleitung in Immobilienentwicklungsunternehmen bis zur Gesamtverantwortung als Head of Real Estate und Architektur bei der Firma Uster AG.
Brückenbauerin zwischen Praxis und Forschung
Parallel zu ihrer praktischen Tätigkeit engagiert sie sich seit vielen Jahren in Forschung und Lehre. Ihre interdisziplinäre Kompetenz, internationale Erfahrung und strategische Denkweise machen sie zu einer Brückenbauerin zwischen Praxis und Forschung in den Bereichen Architektur, Smart Buildings, Smart Cities, Digitalisierung und Nachhaltigkeit.

Implementation of BIM and AI
In this project, Building Information Modeling (BIM) was used to optimize the design and construction processes. BIM allowed for precise modeling of the steep terrain, enabling efficient planning and visualization of the modular structures and their integration into the challenging site conditions. The technology also facilitated seamless coordination among various teams, ensuring sustainability goals were met while maintaining design integrity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) was employed to analyze the environmental impact of materials and construction methods. AI algorithms were used to simulate energy efficiency, assess structural performance, and optimize material usage. This ensured that the project adhered to sustainable practices while achieving a harmonious balance with the natural forested environment. AI also supported decision-making during the design phase, predicting how the prefabricated components would interact and perform in the final assembly, reducing waste and enhancing overall project efficiency.

In our session at CUREM - Center for Urban & Real Estate Management, University of Zurich, we explored strategies for real estate development, particularly from the perspective of investors. The focus was on how digital tools are revolutionizing planning, analysis, and decision-making in the real estate sector.
Key Points from Today’s Discussion:
🔹 Data-Driven Analyses: Tools for market and site analysis (e.g., GIS systems) help investors make informed decisions about locations and target markets.
🔹 Financial Modeling: Tools like Excel with macros or Python scripts enable precise profitability calculations, sensitivity analyses, and scenario simulations.
🔹 Project Visualization: Software like BIM and AI (Building Information Modeling + Artificial Intelligence) enhances project visualization, making it easier for stakeholders to understand and engage.
🔹 Risk Management: Digital tools aid in identifying risks during the early planning stages, leveraging simulations and monitoring market trends.
A key takeaway from the session was that successful real estate investment relies not only on numbers but also on the ability to integrate innovative approaches, anticipate risks, and leverage technological advancements.
Whether analyzing market opportunities, optimizing development processes, or securing financing, digital tools are essential for giving investors a competitive edge.

Digital terrain modelling is transforming the way architects, planners, and engineers interact with the natural world. 🌿 From visualizing complex topographies to simulating realistic landscapes, advanced tools make it easier than ever to shape ideas into reality.
✨ Why Terrain Modelling Matters:
Precision in planning 🌟
Seamless integration with GIS data 📊
Efficient environmental analysis 🌲
Stunning visualizations for impactful presentations 🎥
🎯 Popular Tools to Explore:
AutoCAD Civil 3D: For infrastructure design and drafting.
SketchUp + Plugins: Quick 3D terrain creation.
Rhino + Grasshopper: Precision + automation for custom forms.
ArcGIS: Ideal for GIS-based topographical insights.
💡 Whether you're designing for architecture, urban planning, or ecological restoration, mastering digital terrain modelling opens up a world of possibilities.
Show us your terrain-inspired projects! Drop your designs or tag a fellow creator who’d love this. 📷👇
#DigitalDesign #TerrainModelling #CAD #GIS #Architecture #3DModelling #SustainableDesign

🔹 AI in Design & Planning
Artificial Intelligence played a central role, from generating design concepts to optimizing layouts and material usage. Tools like AI-enhanced visualization software allowed us to experiment with ideas quickly and efficiently, ensuring the final design was both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
🔹 Digital Fabrication & Craftsmanship
Even the physical wooden model—an essential part of architectural competitions—was crafted using digital fabrication techniques, informed by AI-based simulations. This seamless integration of traditional craftsmanship with cutting-edge technologies like 3D printing and precision CNC machining highlights the future of architectural practice.

🔹 Data-Driven Planning for People-Centered Design
The project began with a comprehensive statistical demographic study, analyzing population shifts, age distribution, and economic patterns in the affected areas. These insights informed every decision, ensuring that the reconstructed spaces cater to the actual needs of the community—from housing to public spaces, and even economic infrastructure.
🔹 Handcrafted with Purpose
While data shaped the framework, the project was brought to life through handcrafted techniques that reflect the rich cultural heritage of Onagawa. Local materials and traditional construction methods were used alongside modern technologies, creating structures that honor the past while looking toward the future.
🔹 Rebuilding Lives, Not Just Cities
The project emphasizes community empowerment, involving residents in the reconstruction process. This hands-on approach fosters a sense of ownership and belonging, ensuring that the spaces are more than buildings—they are homes, hubs of connection, and symbols of resilience.
🔹 A Model for Post-Disaster Recovery
The Onagawa Project stands as a beacon of how thoughtful design, powered by statistical rigor and human craftsmanship, can drive meaningful recovery. It demonstrates that rebuilding after a catastrophe is not just about physical infrastructure but also about nurturing the social and cultural fabric of a community.
By blending data-driven insights with the art of human touch, the Onagawa Project showcases the potential to transform tragedy into an opportunity for rebirth, creating spaces that inspire and endure.
#OnagawaProject #PostDisasterRecovery #SustainableReconstruction #FukushimaRecovery #CommunityDrivenDesign #HandcraftedArchitecture #ResilienceThroughDesign

In this groundbreaking project, AI and BIM come together to streamline processes, optimize designs, and ensure seamless collaboration among architects, engineers, and developers. AI’s ability to process vast datasets enables predictive analysis and informed decision-making, from site selection to energy-efficient building designs. Meanwhile, BIM offers an integrated approach to project management, providing a shared platform that fosters real-time coordination and minimizes errors throughout the lifecycle of the development.
Autodesk Forma’s sophisticated tools enhance every phase of the project, from conceptualization to execution, emphasizing sustainability and innovation. By leveraging Archicad’s dynamic design capabilities, the project achieves a balance between aesthetic excellence and functional efficiency, creating spaces that are not just visually appealing but also environmentally responsible.
This Zurich Lake development is more than a construction project—it’s a vision of what’s possible when technology meets creativity, pushing the boundaries of urban planning and sustainable living. Watch the video to explore how AI and BIM are not just supporting construction but fundamentally transforming it, paving the way for smarter, greener, and more integrated communities.
#RealEstateInnovation #AIinConstruction #BIM #ZurichLakeDevelopment #SustainableArchitecture #FutureOfConstruction

Real Estate actors can evaluate material suitability and rapidly see the influence of their design decisions on associated carbon emissions.
The biggest opportunity for technology to manage our carbon footprint is by having tools like Forma, that will allow us to analyze our projects in real time, as we’re designing them.
Being able to have that information, that feedback, as we’re doing the design work is really what’s going to enable us to achieve the goals that we need to reduce the carbon impact of the built environment.

***Learning Outcomes***
1.Understanding AI's Role in Urban Planning and Real Estate Development: Students gain firsthand experience in how AI can optimize complex urban development challenges.
By witnessing the algorithm at work, they see how AI processes constraints and opportunities in ways that are often different from human intuition.
2. Human vs. Machine Thinking: The workshop provides a fascinating contrast between human creativity and machine logic: Students observe the strengths and limitations of both approaches: where human designers bring creativity and empathy to urban planning, the AI focuses on efficiency, rule compliance, and optimization.
3. Legal and Architectural Awareness: Students deepen their understanding of the critical constraints in urban development, such as zoning laws, building codes, environmental considerations, and infrastructure planning. They must apply these in their city designs, just as the AI does.
4. Problem-Solving and Innovation: The course encourages students to think creatively about real-world urban problems. The head-to-head comparison with the AI forces students to consider new approaches, question traditional methods, and innovate in ways that machines cannot.
5. Collaborative and Competitive Learning
The "vs." framework sparks both collaboration and competition. Students learn from each other and from the AI-generated results, fostering an environment of constant iteration, improvement, and learning from mistakes.
6. Future-Proof Skills
Students leave the course equipped with future-proof skills at the intersection of urban planning, architecture, and AI. They understand not only how to design cities, but also how to collaborate with and leverage AI tools in their future careers.
***Key Insights from the Workshop***
At the end of the course, a comparative analysis reveals fascinating insights:
a) Efficiency vs. Creativity: The AI often produces more efficient layouts, optimizing land use and infrastructure. However, human designs tend to reflect more nuanced social and cultural considerations.
b)Legal and Practical Constraints: The AI never overlooks legal constraints, whereas students sometimes need reminders. This demonstrates the importance of integrating AI as a compliance tool in real-world projects.
c)Hybrid Solutions: The most exciting outcome is the realization that the best urban plans emerge from a collaborative human-AI process—leveraging the strengths of both to create sustainable, livable cities.
In essence, this class prepares future architects, urban planners, and Real Estate developers to navigate the rapidly evolving world of real estate and city building, where human expertise and AI tools must work hand-in-hand to shape the cities of tomorrow.

Per 1. September 2025 tritt Dr. Andrea González die Leitung der neu geschaffene Kompetenzgruppe Smart Building Management (SBM) am Institut für Facility Management an. Diese Gruppe beschäftigt sich mit der intelligenten, nachhaltigen und nutzerzentrierten Entwicklung, Nutzung und Bewirtschaftung von Gebäuden und Arealen. Im Fokus stehen digitale Technologien, datenbasierte Services und integrale Strategien entlang des gesamten Immobilienlebenszyklus.
Expertin mit langjähriger Erfahrung weltweit
Andrea González verfügt über mehr als 15 Jahre internationale Erfahrung in den Bereichen Städtebau, Immobilienentwicklung, Architektur, Nachhaltigkeit und Digitalisierung. Dabei hat sie auch komplexe Immobilienprojekte in Europa und Asien umgesetzt. Ihr fundiertes Wissen erstreckt sich über alle Phasen des Immobilienlebenszyklus. Dazu gehören Standortanalyse, Akquisition, Konzeptentwicklung, Planung, Bau, Betrieb und Sanierung sowie die strategische Umnutzung und Verwertung. Besonderen Fokus legt sie auf innovative Smart-Building-Strategien. Ihre Führungserfahrung reicht von der Projektleitung in Immobilienentwicklungsunternehmen bis zur Gesamtverantwortung als Head of Real Estate und Architektur bei der Firma Uster AG.
Brückenbauerin zwischen Praxis und Forschung
Parallel zu ihrer praktischen Tätigkeit engagiert sie sich seit vielen Jahren in Forschung und Lehre. Ihre interdisziplinäre Kompetenz, internationale Erfahrung und strategische Denkweise machen sie zu einer Brückenbauerin zwischen Praxis und Forschung in den Bereichen Architektur, Smart Buildings, Smart Cities, Digitalisierung und Nachhaltigkeit.

Implementation of BIM and AI
In this project, Building Information Modeling (BIM) was used to optimize the design and construction processes. BIM allowed for precise modeling of the steep terrain, enabling efficient planning and visualization of the modular structures and their integration into the challenging site conditions. The technology also facilitated seamless coordination among various teams, ensuring sustainability goals were met while maintaining design integrity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) was employed to analyze the environmental impact of materials and construction methods. AI algorithms were used to simulate energy efficiency, assess structural performance, and optimize material usage. This ensured that the project adhered to sustainable practices while achieving a harmonious balance with the natural forested environment. AI also supported decision-making during the design phase, predicting how the prefabricated components would interact and perform in the final assembly, reducing waste and enhancing overall project efficiency.

In our session at CUREM - Center for Urban & Real Estate Management, University of Zurich, we explored strategies for real estate development, particularly from the perspective of investors. The focus was on how digital tools are revolutionizing planning, analysis, and decision-making in the real estate sector.
Key Points from Today’s Discussion:
🔹 Data-Driven Analyses: Tools for market and site analysis (e.g., GIS systems) help investors make informed decisions about locations and target markets.
🔹 Financial Modeling: Tools like Excel with macros or Python scripts enable precise profitability calculations, sensitivity analyses, and scenario simulations.
🔹 Project Visualization: Software like BIM and AI (Building Information Modeling + Artificial Intelligence) enhances project visualization, making it easier for stakeholders to understand and engage.
🔹 Risk Management: Digital tools aid in identifying risks during the early planning stages, leveraging simulations and monitoring market trends.
A key takeaway from the session was that successful real estate investment relies not only on numbers but also on the ability to integrate innovative approaches, anticipate risks, and leverage technological advancements.
Whether analyzing market opportunities, optimizing development processes, or securing financing, digital tools are essential for giving investors a competitive edge.

Digital terrain modelling is transforming the way architects, planners, and engineers interact with the natural world. 🌿 From visualizing complex topographies to simulating realistic landscapes, advanced tools make it easier than ever to shape ideas into reality.
✨ Why Terrain Modelling Matters:
Precision in planning 🌟
Seamless integration with GIS data 📊
Efficient environmental analysis 🌲
Stunning visualizations for impactful presentations 🎥
🎯 Popular Tools to Explore:
AutoCAD Civil 3D: For infrastructure design and drafting.
SketchUp + Plugins: Quick 3D terrain creation.
Rhino + Grasshopper: Precision + automation for custom forms.
ArcGIS: Ideal for GIS-based topographical insights.
💡 Whether you're designing for architecture, urban planning, or ecological restoration, mastering digital terrain modelling opens up a world of possibilities.
Show us your terrain-inspired projects! Drop your designs or tag a fellow creator who’d love this. 📷👇
#DigitalDesign #TerrainModelling #CAD #GIS #Architecture #3DModelling #SustainableDesign

🔹 AI in Design & Planning
Artificial Intelligence played a central role, from generating design concepts to optimizing layouts and material usage. Tools like AI-enhanced visualization software allowed us to experiment with ideas quickly and efficiently, ensuring the final design was both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
🔹 Digital Fabrication & Craftsmanship
Even the physical wooden model—an essential part of architectural competitions—was crafted using digital fabrication techniques, informed by AI-based simulations. This seamless integration of traditional craftsmanship with cutting-edge technologies like 3D printing and precision CNC machining highlights the future of architectural practice.

🔹 Data-Driven Planning for People-Centered Design
The project began with a comprehensive statistical demographic study, analyzing population shifts, age distribution, and economic patterns in the affected areas. These insights informed every decision, ensuring that the reconstructed spaces cater to the actual needs of the community—from housing to public spaces, and even economic infrastructure.
🔹 Handcrafted with Purpose
While data shaped the framework, the project was brought to life through handcrafted techniques that reflect the rich cultural heritage of Onagawa. Local materials and traditional construction methods were used alongside modern technologies, creating structures that honor the past while looking toward the future.
🔹 Rebuilding Lives, Not Just Cities
The project emphasizes community empowerment, involving residents in the reconstruction process. This hands-on approach fosters a sense of ownership and belonging, ensuring that the spaces are more than buildings—they are homes, hubs of connection, and symbols of resilience.
🔹 A Model for Post-Disaster Recovery
The Onagawa Project stands as a beacon of how thoughtful design, powered by statistical rigor and human craftsmanship, can drive meaningful recovery. It demonstrates that rebuilding after a catastrophe is not just about physical infrastructure but also about nurturing the social and cultural fabric of a community.
By blending data-driven insights with the art of human touch, the Onagawa Project showcases the potential to transform tragedy into an opportunity for rebirth, creating spaces that inspire and endure.
#OnagawaProject #PostDisasterRecovery #SustainableReconstruction #FukushimaRecovery #CommunityDrivenDesign #HandcraftedArchitecture #ResilienceThroughDesign

In this groundbreaking project, AI and BIM come together to streamline processes, optimize designs, and ensure seamless collaboration among architects, engineers, and developers. AI’s ability to process vast datasets enables predictive analysis and informed decision-making, from site selection to energy-efficient building designs. Meanwhile, BIM offers an integrated approach to project management, providing a shared platform that fosters real-time coordination and minimizes errors throughout the lifecycle of the development.
Autodesk Forma’s sophisticated tools enhance every phase of the project, from conceptualization to execution, emphasizing sustainability and innovation. By leveraging Archicad’s dynamic design capabilities, the project achieves a balance between aesthetic excellence and functional efficiency, creating spaces that are not just visually appealing but also environmentally responsible.
This Zurich Lake development is more than a construction project—it’s a vision of what’s possible when technology meets creativity, pushing the boundaries of urban planning and sustainable living. Watch the video to explore how AI and BIM are not just supporting construction but fundamentally transforming it, paving the way for smarter, greener, and more integrated communities.
#RealEstateInnovation #AIinConstruction #BIM #ZurichLakeDevelopment #SustainableArchitecture #FutureOfConstruction
Welcome to this professional hub. I am a passionate real estate developer, educator, and advocate for the future of construction and design. With expertise at the intersection of real estate, digitalization, sustainability, artificial intelligence, and collaborative tools like BIM, I bridge the gap between traditional craftsmanship and cutting-edge technologies.
In my work, I integrate the timeless art of manual craftsmanship, such as woodworking, with the power of modern digital tools, creating a seamless connection between the hands-on and the high-tech. Whether through innovative real estate development projects, immersive teaching experiences, or impactful publications, my goal is to redefine how we build and interact with our built environment.
Explore my projects, teaching materials, and publications to discover how I am shaping the future of construction, technology, and collaboration. Let's create the future of building — where craftsmanship meets innovation.
Projects
The real estate industry is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by the forces of digitalization, sustainability, and data-driven decision-making. To provide valuable insights into these changes, we have created the Zeitgeist Real Estate Knowledge Hub, a platform dedicated to exploring the latest developments in smart building management for real estate development, asset and portfolio management, and sustainable practices.
This hub, anchored at the ZHAW Zurich University of Applied Sciences offers access to cutting-edge research that delves into emerging trends, such as the integration of AI-driven tools, the adoption of sustainable construction technologies, and the role of digital solutions like Data Ontologies or Building Information Modeling (BIM) in streamlining processes. It also provides practical insights into optimizing portfolios, managing risk, and achieving superior returns on investment through innovative strategies.
A significant focus of the hub is on highlighting how technologies like machine learning, IoT, and advanced analytics are reshaping the way real estate projects are conceived, developed, and managed. By fostering collaboration and innovation, it aims to inspire new approaches that drive progress and contribute to a more sustainable and efficient future in real estate.
Here some of our latest projects:

Real Estate Development Steinacherstrasse

Office building space in Zhengzhou, China

3rd Prize competition School Breite in Muttenz

Real Estate Development in Richterswil

Coworking Hub Ai in Real Estate for Gärtnerstrasse, 2 in Basel

Re-Development Miikron

Shanghai Resort Digitally Handcrafted
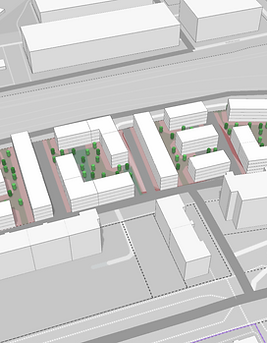
Data-based Urban Planning at ETH

1st Prize competition Housing in Badenerstrasse

Integrierte Abwicklungsmodelle aus der Perspektive der Bauherrschaft

School Visp competition

Onagawa Housing in Japan

Real Estate Development Hubengarten

Studienauftrag Obermeilen Redevelopment

Digital Werkstatt with ETH, HSLU, HWZ, and ZHAW

SNSF Project Kleinwohnformen HSLU

Real Estate Development Bonstetten

Sustainability and Digitalization with ETH STL

Coworking Hub Ai in Real Estate for Wankdorffeldstrasse in Basel

Contact for more references
Publications
Zeitgeist Real Estate is a dedicated platform for sharing publications and research that address the rapidly evolving landscape of real estate development, asset and portfolio management, digital transformation, and sustainability. In an industry shaped by technological advancements and growing environmental concerns, the hub aims to contribute to meaningful discourse by publishing thought leadership, academic studies, and practical insights from industry professionals.
This platform focuses on fostering a deeper understanding of how digital tools, such as AI, machine learning, and Building Information Modeling (BIM), are revolutionizing traditional practices in real estate. Publications highlight innovative approaches to optimizing portfolios, improving operational efficiency, and making data-driven decisions that maximize returns while addressing regulatory and environmental challenges.
By publishing articles that provide actionable insights, the hub promotes responsible development and portfolio management practices aligned with long-term sustainability goals. The hub serves as a resource for those looking to stay informed about emerging trends and best practices in real estate. It also offers a platform for exchanging ideas and advancing the conversation on how technology and sustainability can redefine the built environment for future generations.
Here some of our latest publications:

Adaptative Reuse of Historical Buildings in Switzerland: Predictive Analysis and AI

Assessment of the quality of the view by means of crowdsourcing and deep learning

Sustainability and Digitalization: Cooperative planning in Switzerland

Evaluating the impact of flexible offices in coping with uncertainty in future demand

Japan: two years after the tsunami. Participative processes

Flexibility of Space and Digital Representation: Villas and Gardens of Tokyo

Künstliche Intelligenz für den Wiederaufbau von Kulturgütern

Evaluating the impact of flexible offices in coping with the uncertain future demand

Preparing the Urban Space for the age of distributed work

Statistical Approach to Asset Redevelopment (Renovation, Demolition and Reconstruction)

Künstliche Intelligenz für den Wiederaufbau von Kulturgütern

Predictive Analysis and Dynamic Building Simulation via AI

Optimierungsstrategien im Nutzungszyklus von Immobilien

High-Speed rail, market access, and the rise of consumer cities: Evidence from China

Assessing the learning of the students in a course that links praxis and theory

KI in der Immobilienwirtschaft

Kleinwohnformen: Wohn- und Lebensraum mit Potenzial?

Künstliche Intelligenz für den Wiederaufbau von Kulturgütern

Digitalizacion urbana o el urbanismo 4.0

Cities, Urban Planning and Architecture

Japan: Two years after the Tsunami

Smart Re-cycle and Upcycle Construction Strategies

The Territory Inhabited: Resilient Cities

Smart Cities in the reconstruction of Tohoku: an Interview

Contact for more References
Press
Here some of our latest press releases:

El Mundo - Arquitectura para volver a vivir

La Nueva Espana - Smart Building Management in Japan

La Nueva Espana - Life in between two lines

SVIT - KI in der Immobilienwirtschaft

La Nueva Espana - The Termometer

SVIT - KI in der Immobilienwirstchaft

ZHAW - Andrea Gonzalez übernimmt Leitung SBM

Gebäudetechnik - Leitung Kompetenzgruppe Smart Building Management

Netzwoche - Andrea Gonzalez Leiterin Smart Building Management

ZHAW - Leitung Kompetenzgruppe Smart Building Management
Teaching
Zeitgeist Real Estate Learning Hub also explore innovative teaching methodologies and the evolving intersection of digital and hands-on learning experiences. In a world where education is being transformed by technology and new pedagogical approaches, this hub aims to contribute to meaningful discourse by teaching about digital practices thought leadership, academic studies, and practical insights from educators and learning designers.
Our platform emphasizes the synergy between digital tools and physical, experiential learning—a symbiosis that enhances engagement and retention that we call "Digital Workshops". By incorporating technologies like AI, BIM, interactive simulations, and augmented reality into gamified learning processes, we foster dynamic, immersive educational environments that bridge the gap between theory and practice.
Our classes focus on gamification strategies that make learning more interactive, engaging, and impactful, while showcasing how digital tools can complement traditional working methods. We highlight approaches that help learners develop critical skills through problem-solving, collaboration, and hands-on projects, ensuring they are equipped for real-world challenges.
By providing actionable insights on innovative teaching practices, the hub promotes inclusive, future-ready education that balances digital fluency with tactile, experiential learning. We serve as a resource for educators seeking to stay informed about emerging trends in pedagogy and offer a platform for exchanging ideas on how technology can enhance learning experiences across disciplines.
For over the last 15 years our classes and research have been held at the following institutions: Tokyo Institute of Technology (TIT), Tongji University in Shanghai (Tongji), American University in Dubai (AUD), Universidad Politecnica de Madrid (UPM), Colegio oficial de Arquitectos de Madrid y Asturias (COAM / COAA), Universidad Francisco de Vitoria (UFV), Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich (ETH Zurich), University of Liechtenstein, Lucerne University of Applied Sciences and Arts (HSLU), Zurich University of Applied Sciences (ZHAW) and of Applied Sciences in Business Administration (HWZ), Center for Urban and Real Estate Management of Zurich (CUREM) and the Swiss Association of Real Estate Industry (SVIT) among other and here some of our latest topics:





















"One of the best (if not the best) seminar I have ever visited"
Student, Lecture at SVIT on AI in Real Estate Development
We are repeating our workshop "Digitally Handcrafted" with BIM & AI in 2025
The workshop incorporates modern technologies, including Building Information Modeling (BIM) and Artificial Intelligence (AI), to analyze, simulate, and optimize wooden traditional construction methods. These tools were used to enhance the understanding of structural forces, material behavior, and the precision required in replicating the craftsmanship of traditional wood construction techniques. The use of these components in construction is grounded in the natural preservation of the balance of forces, carefully managing shear, bending, torsion, and compression stresses while accounting for material shrinkage.

About
My name is Dr. Andrea Gonzalez
I am an architect, smart building and real estate manager with an MBA and a doctorate in real estate development, combining expertise in real estate, architecture, urban planning, data science, and academia. My work focuses on integrating technological innovation to create forward-thinking, sustainable solutions for the built environment. With professional experience in Japan, China, Spain, and Switzerland, I bring a global, intercultural perspective to my projects and academic endeavors.
Understanding the cultural, social, and technical nuances of different contexts has been essential in shaping my approach to urban design and real estate development. In academia, I have held teaching and research roles at leading institutions, including ETH Zurich and University of Liechtenstein, among other and have been a guest lecturer and researcher at several national and international universities.
From the professional side, I have been head of real estate, as well as team leader and project leader in the same field for several years in Switzerland and abroad. Sharing insights with students and professionals is a core part of my work, fostering critical thinking about the future of cities and buildings.
My practice and research focuses on the intersections of digitalization, artificial intelligence, sustainability, real estate, asset and portfolio management, architecture, and urban planning. Through all this, I aim to bridge theory and application to address the challenges of modern urban environments and drive meaningful change in urban and real estate development.




